Advancements in Diabetes Treatment: Exploring Stem Cell Therapy in India
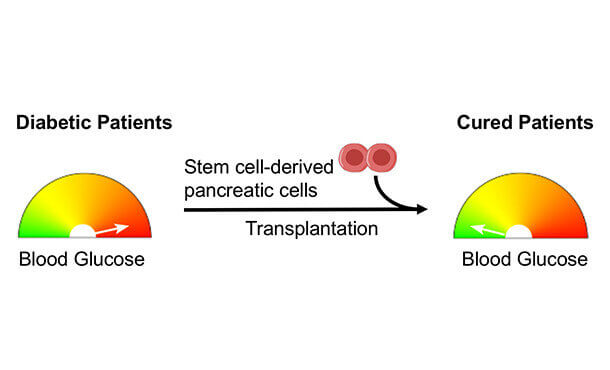
Diabetes Stem Cell Treatment India, Muscular Dystrophy Stem Cell Treatment India :Diabetes mellitus, a chronic metabolic disorder characterized by elevated blood sugar levels, poses significant health challenges worldwide. While conventional treatments such as insulin therapy and oral medications help manage diabetes, they do not address the underlying cause of the disease or prevent its progression. In recent years, researchers and clinicians have turned to stem cell therapy as a potential alternative for treating diabetes, offering new hope to millions of patients globally, including those in India.
Stem cell therapy holds promise as a revolutionary approach for treating diabetes by targeting the root cause of the disease: the loss or dysfunction of insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. Through the use of stem cells, which have the unique ability to differentiate into various cell types, including insulin-producing beta cells, this innovative therapy aims to regenerate damaged pancreatic tissue, restore normal insulin production, and improve blood sugar control.
In India, several medical institutions, hospitals, and research centers are at the forefront of pioneering stem cell-based treatments for diabetes. These initiatives typically involve the following key components:
Patient Evaluation and Selection
Individuals with diabetes undergo comprehensive medical assessments and evaluations to determine their eligibility and suitability for stem cell therapy. This includes reviewing medical history, conducting physical examinations, assessing diabetes-related complications, and performing laboratory tests to evaluate pancreatic function and beta cell mass.
- Stem Cell Source and Preparation: Stem cells used for diabetes treatment can be obtained from various sources, including adipose tissue (fat), bone marrow, umbilical cord blood, and placental tissue. Each source offers unique advantages in terms of accessibility, safety, and regenerative potential. The harvested stem cells are then processed, purified, and cultured to enhance their therapeutic properties and optimize their ability to differentiate into insulin-producing beta cells.
- Stem Cell Administration: The enriched stem cells are administered to the patient via various routes, depending on the specific treatment protocol and patient’s condition. Common delivery methods include intravenous infusion, intrapancreatic injection, and implantation at the site of pancreatic injury or dysfunction. These approaches aim to promote the regeneration of pancreatic tissue, stimulate insulin production, and improve glucose metabolism.
- Monitoring and Follow-Up: Following stem cell therapy, patients undergo regular monitoring and follow-up assessments to evaluate treatment outcomes, glycemic control, and any potential adverse effects. This includes measuring blood sugar levels, assessing insulin requirements, monitoring diabetes-related complications, and documenting improvements in quality of life. Additional interventions or adjustments to treatment may be recommended based on individual response and clinical outcomes.
While stem cell therapy for diabetes represents a promising avenue for treatment, it is important to recognize that research in this field is still evolving, and clinical evidence supporting its efficacy is limited. Further randomized controlled trials, long-term studies, and regulatory approvals are needed to establish the safety, effectiveness, and optimal treatment protocols for stem cell therapy in diabetes.
Despite these challenges, the ongoing research and clinical efforts in India and around the world offer hope for the development of innovative therapies that may one day transform the management and treatment of diabetes. With continued advancements in stem cell technology, there is optimism that stem cell therapy may emerge as a valuable addition to the existing treatment options for diabetes, providing new opportunities for improved glycemic control, reduced reliance on insulin, and enhanced quality of life for patients.